System Development: 7 Ultimate Secrets for Success
System development isn’t just about coding—it’s about crafting intelligent, scalable solutions that transform how businesses operate. From startups to Fortune 500s, mastering this process is the key to innovation, efficiency, and long-term growth.
What Is System Development and Why It Matters

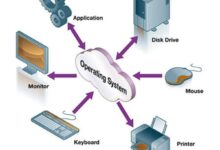
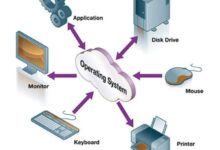
At its core, system development refers to the structured process of designing, building, testing, and deploying information systems to meet specific organizational needs. Whether it’s a customer relationship management (CRM) tool or an enterprise resource planning (ERP) platform, system development turns abstract ideas into functional digital realities.
The Evolution of System Development
System development has come a long way since the early days of computing. In the 1960s and 70s, development was largely linear and rigid, following what we now call the Waterfall model. As technology evolved, so did methodologies—giving rise to agile, DevOps, and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) practices.
- 1960s–1980s: Waterfall dominated with sequential phases
- 1990s: Rise of object-oriented programming and prototyping
- 2000s–Present: Agile, Scrum, and Lean methodologies take center stage
Today, system development is more dynamic than ever, integrating cloud computing, AI, and real-time analytics into the development lifecycle. According to the IEEE Computer Society, modern system development must be adaptive, user-centric, and secure by design.
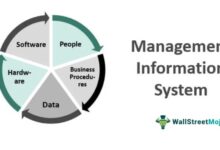
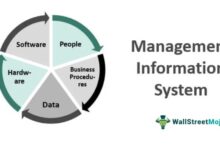
Key Components of a Development System
A successful system development project relies on several interconnected components that ensure functionality, reliability, and scalability.
Requirements Gathering: Understanding what stakeholders need from the system.Design Architecture: Creating blueprints for data flow, user interface, and backend logic.Development Environment: Tools, frameworks, and platforms used to write and test code.Testing & Validation: Ensuring the system works as intended under various conditions.Deployment & Maintenance: Launching the system and providing ongoing support.
.”A system is never just software—it’s people, processes, and technology working in harmony.” — Dr.Linda Rising, Software Engineering Expert
The 7 Phases of System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
The System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a foundational framework used to plan, create, test, and deploy information systems.It provides a clear roadmap, ensuring projects stay on track, within budget, and aligned with business goals.Each phase builds upon the previous one, creating a structured yet flexible approach to system development..
1. Planning and Feasibility Analysis
This initial phase determines whether a proposed system is worth pursuing. It involves assessing technical, economic, operational, and legal feasibility.
- Technical Feasibility: Can the organization build or acquire the necessary technology?
- Economic Feasibility: Will the benefits outweigh the costs?
- Operational Feasibility: Will users adopt and effectively use the system?
Stakeholders, project managers, and IT consultants collaborate to define project scope, objectives, and constraints. Tools like SWOT analysis and cost-benefit models are commonly used. The output is a feasibility report that guides decision-making.
2. Requirements Analysis
This phase dives deep into what the system must do. It’s where developers gather detailed input from end-users, clients, and business analysts to define functional and non-functional requirements.
- Functional Requirements: Features like login systems, data processing, reporting tools.
- Non-Functional Requirements: Performance, security, scalability, and usability standards.
Techniques such as interviews, surveys, use case modeling, and user stories help capture accurate needs. Missteps here often lead to costly rework later. As noted by the British Computer Society, over 60% of project failures stem from poor requirement gathering.
3. System Design
With requirements in hand, the design phase translates them into a technical blueprint. This includes both high-level architecture and detailed component specifications.
- Architectural Design: Defines system layers (presentation, business logic, data access).
- Database Design: ER diagrams, schema, normalization.
- UI/UX Design: Wireframes, prototypes, and user interaction flows.
Design documents serve as a contract between developers and stakeholders. They reduce ambiguity and ensure everyone shares the same vision. Modern tools like Figma, Lucidchart, and UML modeling software streamline this process.
4. Development and Coding
This is where the actual building happens. Developers write code based on the design specifications using programming languages, frameworks, and development environments suited to the project.
- Frontend: HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React, Angular
- Backend: Python, Java, Node.js, .NET
- Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB
Version control systems like Git ensure collaboration and code integrity. Continuous integration tools (e.g., Jenkins, GitHub Actions) automate testing and deployment workflows. The goal is clean, maintainable, and secure code that aligns with best practices.
5. Testing and Quality Assurance
No system is ready without rigorous testing. This phase identifies bugs, performance bottlenecks, and security vulnerabilities before deployment.
- Unit Testing: Individual components are tested in isolation.
- Integration Testing: Ensures modules work together seamlessly.
- System Testing: Validates the complete system against requirements.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): End-users verify the system meets their needs.
Automated testing frameworks like Selenium, JUnit, and Cypress improve efficiency and coverage. According to Guru99, effective QA can reduce post-launch defects by up to 80%.
6. Deployment
Once testing is complete, the system goes live. Deployment strategies vary depending on risk tolerance and system complexity.
- Big Bang Deployment: Full switch at once (high risk, fast).
- Phased Deployment: Roll out features gradually.
- Parallel Running: Old and new systems run simultaneously during transition.
Cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud simplify deployment with scalable infrastructure and automated scaling. Proper training and documentation are critical to ensure smooth adoption.
7. Maintenance and Evaluation
Deployment isn’t the end—it’s the beginning of the maintenance phase. Systems require updates, bug fixes, performance tuning, and feature enhancements.
- Corrective Maintenance: Fixing issues discovered post-launch.
- Adaptive Maintenance: Updating for new environments (e.g., OS upgrades).
- Perfective Maintenance: Improving performance or usability.
- Preventive Maintenance: Proactively addressing potential failures.
Feedback loops from users help prioritize improvements. Regular audits ensure the system remains aligned with business goals. As technology evolves, so must the system.
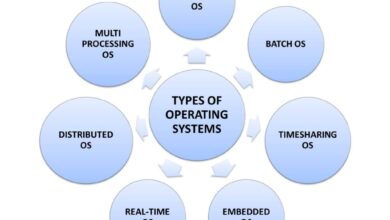
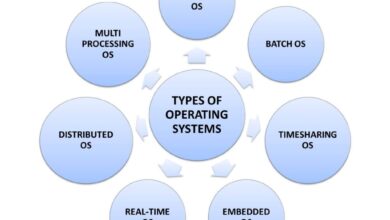
Popular System Development Methodologies Compared
Choosing the right methodology is crucial for project success. Different approaches suit different types of projects, teams, and organizational cultures. Let’s explore the most widely used models in modern system development.
Waterfall Model: The Classic Approach
The Waterfall model is a linear, sequential approach where each phase must be completed before the next begins. It’s one of the oldest and most structured methodologies.
- Clear milestones and deliverables
- Easy to manage due to rigid structure
- Ideal for projects with well-defined requirements
However, it lacks flexibility. Changes are difficult and expensive once the project is underway. It’s best suited for small, predictable projects like government systems or embedded software. Learn more about its pros and cons at TutorialsPoint.
Agile Methodology: Flexibility and Speed
Agile is an iterative approach that emphasizes collaboration, customer feedback, and rapid delivery. Instead of a single final product, Agile delivers working software in small increments called sprints.
- High adaptability to changing requirements
- Frequent releases and stakeholder involvement
- Improved team morale and productivity
Frameworks like Scrum and Kanban are subsets of Agile. Daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives keep teams aligned. Agile is ideal for startups, digital products, and fast-moving industries. The Agile Alliance reports that 71% of organizations use Agile in some form.
DevOps: Bridging Development and Operations
DevOps is not just a methodology—it’s a cultural shift that integrates development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) to shorten the system development lifecycle and deliver high-quality software continuously.
- Automated testing and deployment pipelines
- Continuous monitoring and feedback
- Improved collaboration between teams
Tools like Docker, Kubernetes, Jenkins, and Ansible enable infrastructure as code (IaC) and seamless deployment. DevOps reduces time-to-market and increases system reliability. Companies like Netflix and Amazon rely heavily on DevOps for scalability and resilience.
Essential Tools and Technologies in System Development
The right tools can make or break a system development project. From planning to deployment, modern developers rely on a robust ecosystem of software and platforms to streamline workflows and enhance productivity.
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)
IDEs are the central hub for coding, debugging, and testing. They combine code editors, compilers, and debuggers into a single application.
- Visual Studio Code: Lightweight, extensible, supports multiple languages.
- IntelliJ IDEA: Popular for Java and enterprise applications.
- PyCharm: Tailored for Python development.
- Eclipse: Open-source, widely used in academic and enterprise settings.
These tools boost efficiency with features like syntax highlighting, auto-completion, and real-time error detection.
Version Control Systems
Version control is essential for managing code changes, especially in team environments. It allows developers to track modifications, revert to previous versions, and collaborate without conflicts.
- Git: The most popular distributed version control system.
- GitHub: Cloud-based platform for hosting Git repositories and collaboration.
- GitLab: Offers CI/CD integration and DevOps capabilities.
- Bitbucket: Integrated with Jira for agile project management.
According to GitHub’s Octoverse Report, over 100 million developers use Git worldwide, making it the de facto standard in system development.
Project Management and Collaboration Tools
Effective communication and task tracking are vital for successful system development. These tools help teams stay organized and aligned.
- Jira: Powerful for agile project tracking and issue management.
- Trello: Visual Kanban boards for task organization.
- Asana: Task and workflow management for cross-functional teams.
- Slack: Real-time messaging and integration with development tools.
Integration with CI/CD pipelines and code repositories ensures seamless workflow from idea to deployment.
Best Practices for Successful System Development
While tools and methodologies matter, following proven best practices ensures long-term success in system development. These principles apply across industries and project sizes.
Start with Clear Requirements
Vague or incomplete requirements are the top cause of project failure. Invest time upfront to gather detailed, unambiguous specifications from all stakeholders.
- Use requirement traceability matrices to link features to business goals.
- Validate requirements with prototypes or mockups.
- Document everything to avoid scope creep.
As the Project Management Institute (PMI) states, projects with well-defined requirements are 2.5x more likely to succeed.
Prioritize Security from Day One
Security shouldn’t be an afterthought. With cyber threats rising, integrating security into every phase of system development is non-negotiable.
- Adopt Secure Software Development Lifecycle (SSDLC) practices.
- Conduct regular code reviews and penetration testing.
- Use encryption, authentication, and role-based access control.
The OWASP Top 10 list highlights common vulnerabilities like injection attacks and broken authentication—critical knowledge for any development team.
Embrace Automation
Manual processes are slow and error-prone. Automation accelerates development, improves consistency, and frees developers for higher-value tasks.
- Automate testing with frameworks like Selenium and Jest.
- Use CI/CD pipelines to deploy code automatically upon passing tests.
- Implement infrastructure as code (IaC) using Terraform or CloudFormation.
Companies that automate 80% or more of their testing report 50% faster release cycles, according to a Capgemini study.
Common Challenges in System Development and How to Overcome Them
Even with the best plans, system development projects face obstacles. Recognizing these challenges early allows teams to mitigate risks and stay on course.
Scope Creep: The Silent Project Killer
Scope creep occurs when new features or changes are added without adjusting timelines or budgets. It’s one of the most common reasons for delays and budget overruns.
- Establish a formal change control process.
- Define project scope clearly in the charter.
- Use agile sprints to prioritize and manage new requests.
Regular stakeholder reviews help keep expectations aligned and prevent uncontrolled expansion.
Poor Communication Between Teams
Miscommunication between developers, testers, and business units leads to misunderstandings, rework, and frustration.
- Hold daily stand-up meetings to synchronize progress.
- Use collaborative tools like Confluence for documentation.
- Encourage cross-functional team participation in planning.
Transparent communication builds trust and ensures everyone is working toward the same goal.
Technical Debt Accumulation
Technical debt refers to shortcuts taken during development that compromise code quality. While sometimes necessary, unchecked debt slows future development.
- Refactor code regularly to improve maintainability.
- Track technical debt in issue trackers like Jira.
- Allocate time in sprints for debt reduction.
“Technical debt is like financial debt—it’s okay if managed, but dangerous if ignored.” — Martin Fowler, Chief Scientist at ThoughtWorks
The Future of System Development: Trends to Watch
System development is evolving rapidly, driven by advances in AI, cloud computing, and user expectations. Staying ahead of trends ensures your systems remain competitive and future-proof.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
AI is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s embedded in modern system development. From chatbots to predictive analytics, AI enhances functionality and user experience.
- AI-powered code assistants (e.g., GitHub Copilot) boost developer productivity.
- Machine learning models automate decision-making in applications.
- Natural language processing improves user interfaces.
As AI tools become more accessible, expect wider adoption across industries—from healthcare to finance.
Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
These platforms allow non-developers to build applications using drag-and-drop interfaces, reducing dependency on IT teams.
- OutSystems, Mendix, and Microsoft Power Apps lead the market.
- Speed up prototyping and internal tool development.
- Empower citizen developers while maintaining governance.
According to Gartner, low-code will account for over 65% of application development by 2025.
Cloud-Native Development
Cloud-native approaches build systems specifically for cloud environments, leveraging microservices, containers, and serverless architectures.
- Microservices enable modular, scalable systems.
- Containers (Docker) and orchestration (Kubernetes) ensure portability.
- Serverless computing reduces infrastructure management overhead.
Cloud-native development supports rapid iteration and global scalability—key for digital transformation.
What is system development?
System development is the process of creating, designing, testing, and deploying information systems to meet specific business or user needs. It involves multiple phases, including planning, analysis, design, coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
What are the main phases of SDLC?
The System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) consists of seven key phases: 1) Planning, 2) Requirements Analysis, 3) System Design, 4) Development, 5) Testing, 6) Deployment, and 7) Maintenance. Each phase ensures structured progression toward a functional system.
Which methodology is best for system development?
The best methodology depends on the project. Waterfall suits well-defined, stable projects. Agile is ideal for dynamic environments needing frequent updates. DevOps excels in continuous delivery and automation. Many organizations use hybrid models tailored to their needs.
How important is security in system development?
Security is critical. Integrating security from the start—known as ‘shift-left security’—helps prevent vulnerabilities. Practices like code reviews, penetration testing, and using secure frameworks reduce the risk of breaches and ensure compliance.
What tools are essential for system development?
Essential tools include IDEs (e.g., VS Code), version control (Git/GitHub), project management (Jira), testing frameworks (Selenium), and CI/CD platforms (Jenkins). Cloud platforms like AWS and Azure are also vital for modern deployment.
System development is a complex but rewarding journey that blends technical skill, strategic planning, and user focus. From understanding requirements to maintaining systems post-launch, each phase plays a vital role in delivering value. By embracing proven methodologies, leveraging powerful tools, and staying ahead of trends like AI and cloud-native development, organizations can build robust, scalable, and future-ready systems. The key is continuous learning, collaboration, and a commitment to quality at every stage.
Further Reading: