Systems manager: Systems Manager: 7 Ultimate Power Roles Revealed
Ever wondered who keeps the digital backbone of a company running smoothly? Meet the systems manager — the unsung hero orchestrating technology, teams, and strategy behind the scenes. This role isn’t just about fixing servers; it’s about driving innovation, ensuring security, and aligning IT with business goals.
What Is a Systems Manager? The Core Definition

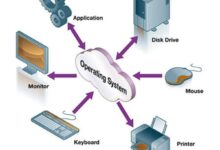
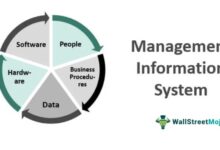
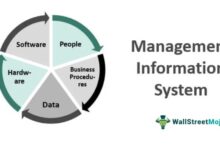
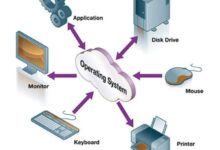
A systems manager plays a pivotal role in modern organizations, acting as the central figure responsible for overseeing an organization’s IT infrastructure. This includes hardware, software, networks, and cloud systems. Their job is not only technical but also strategic, ensuring that technology supports business operations efficiently and securely.
Primary Responsibilities of a Systems Manager
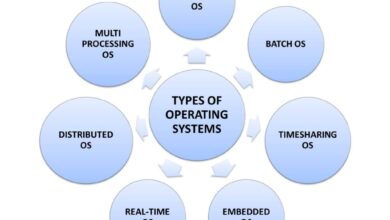
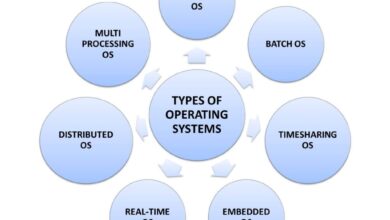
The role of a systems manager spans multiple domains. They are tasked with planning, implementing, and maintaining IT systems that support daily operations. This includes managing operating systems, databases, virtualization platforms, and security protocols.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Overseeing system installations and upgrades
- Monitoring network performance and uptime
- Ensuring data integrity and disaster recovery readiness
- Coordinating with cybersecurity teams to enforce policies
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment in IT management roles is projected to grow 10% from 2021 to 2031, faster than average, highlighting the increasing demand for skilled systems managers.
How It Differs From Similar Roles
While often confused with roles like network administrators or IT directors, a systems manager has a more holistic focus. Unlike a network administrator who primarily handles connectivity, a systems manager oversees the entire ecosystem — from servers to cloud platforms.
Systems Manager vs.Network Administrator: The former manages end-to-end system health; the latter focuses on network traffic and connectivity.Systems Manager vs.IT Director: The IT director handles broader organizational strategy, while the systems manager executes technical operations.Systems Manager vs.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
.DevOps Engineer: DevOps emphasizes automation and development pipelines; systems managers ensure stability and scalability.”A systems manager is the bridge between technology and business outcomes — they don’t just maintain systems, they optimize them.” — TechTarget, 2023
Key Responsibilities of a Systems Manager
The day-to-day duties of a systems manager are diverse and dynamic.They must balance proactive maintenance with reactive troubleshooting, all while aligning with long-term business objectives.Their work ensures that employees can access the tools they need without interruption..
System Maintenance and Optimization
One of the core functions of a systems manager is routine maintenance. This includes applying patches, updating software, and optimizing server performance. Regular audits help identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies in the system.
- Scheduling regular system updates during low-traffic hours
- Conducting performance benchmarking across servers
- Implementing automation scripts to reduce manual tasks
For example, a systems manager might use tools like Nagios or Zabbix to monitor CPU usage, memory leaks, or disk I/O across hundreds of machines simultaneously.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Security Management and Compliance
With cyber threats on the rise, systems managers are frontline defenders of organizational data. They implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols to safeguard sensitive information.
- Enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA) across user accounts
- Conducting regular vulnerability scans using tools like Nessus
- Ensuring compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) provides guidelines that systems managers often follow to strengthen organizational defenses.
Essential Skills for a Successful Systems Manager
To thrive in this role, a systems manager must possess a blend of technical expertise, problem-solving ability, and leadership qualities. The complexity of modern IT environments demands both depth and breadth of knowledge.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Technical Proficiency
A strong foundation in operating systems (Windows, Linux, Unix), virtualization (VMware, Hyper-V), and cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) is essential. Systems managers must also be fluent in scripting languages like Python, Bash, or PowerShell to automate repetitive tasks.
- Expertise in containerization technologies like Docker and Kubernetes
- Familiarity with configuration management tools such as Ansible or Puppet
- Understanding of database systems (SQL, NoSQL) and backup strategies
Platforms like Coursera offer specialized courses to help aspiring systems managers build these competencies.
Problem-Solving and Analytical Thinking
When a critical server goes down, the systems manager must quickly diagnose the root cause. This requires analytical thinking and the ability to interpret logs, error messages, and performance metrics under pressure.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Using root cause analysis (RCA) frameworks after system failures
- Applying logic trees to isolate issues in complex environments
- Simulating failure scenarios through stress testing
“The best systems managers don’t just fix problems — they anticipate them.” — IEEE Computer Society
Systems Manager in Different Industries
The role of a systems manager varies significantly depending on the industry. While the core responsibilities remain consistent, the context and priorities shift based on sector-specific needs.
Healthcare Sector
In healthcare, systems managers are responsible for maintaining electronic health record (EHR) systems, ensuring HIPAA compliance, and securing patient data. Downtime in medical systems can literally be life-threatening, so reliability is paramount.
- Managing EHR platforms like Epic or Cerner
- Implementing audit trails for data access
- Coordinating with medical staff to minimize disruption during upgrades
The Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) sets standards that systems managers in this field must adhere to.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Financial Services
Banks and financial institutions rely heavily on real-time transaction processing. A systems manager here ensures high availability, low latency, and strict regulatory compliance (e.g., PCI-DSS).
- Monitoring trading platform uptime 24/7
- Securing customer financial data with end-to-end encryption
- Conducting penetration tests to identify vulnerabilities
Any delay or breach can result in massive financial loss or reputational damage, making the systems manager’s role critical.
Tools and Technologies Used by Systems Managers
Modern systems managers rely on a wide array of tools to monitor, manage, and secure IT environments. These tools increase efficiency, reduce human error, and provide real-time insights into system health.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Monitoring and Management Platforms
Tools like SolarWinds, PRTG, and Datadog allow systems managers to visualize network performance, track resource usage, and receive alerts when anomalies occur.
- SolarWinds: Offers comprehensive network and system monitoring
- Datadog: Provides cloud-scale monitoring with AI-driven insights
- Zabbix: Open-source alternative with strong community support
These platforms integrate with existing infrastructure to provide a unified view of system status.
Automation and Configuration Tools
To manage large-scale deployments, systems managers use automation tools to standardize configurations and reduce manual intervention.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Ansible: Agentless automation for configuration management
- Puppet: Centralized control over thousands of nodes
- Terraform: Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for cloud provisioning
According to a Puppet State of DevOps Report, organizations using automation see 2x faster deployment rates and 50% fewer change failures.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Becoming a systems manager typically follows a progression from entry-level IT roles. With experience and certifications, professionals can advance into senior technical or leadership positions.
Typical Career Progression
Most systems managers start as help desk technicians, system administrators, or network engineers. Over time, they gain experience in managing larger systems and leading small teams.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Entry-Level: Help Desk Technician or Junior Admin
- Mid-Level: System Administrator or Network Engineer
- Senior Role: Systems Manager or IT Operations Lead
- Executive Level: IT Director or CTO
Each step requires deeper technical knowledge and stronger leadership skills.
In-Demand Certifications
Earning industry-recognized certifications can accelerate career growth and validate expertise. Some of the most valuable include:
- CompTIA Server+: Covers server hardware, storage, and disaster recovery
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator Associate: Focuses on cloud management
- Red Hat Certified Engineer (RHCE): Validates Linux system administration skills
- CISMP (Certified Information Security Manager): For those focusing on security compliance
The CompTIA and Microsoft Learning portals offer structured paths to obtain these credentials.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Challenges Faced by Systems Managers Today
Despite the rewards, the role of a systems manager comes with significant challenges. Rapid technological change, security threats, and organizational pressure make this a high-stress position.
Keeping Up With Technological Change
New technologies emerge constantly — from edge computing to AI-driven operations. Systems managers must continuously learn and adapt to stay relevant.
- Learning curve associated with AI-powered monitoring tools
- Integrating legacy systems with modern cloud platforms
- Managing hybrid environments (on-premise + cloud)
According to Gartner, by 2025, 95% of new IT workloads will be deployed on cloud-native platforms, requiring systems managers to master containerization and microservices.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Balancing Security and Usability
One of the toughest balancing acts is enforcing strict security policies without hindering productivity. Overly restrictive access controls can frustrate employees, while lax policies invite breaches.
- Implementing Zero Trust Architecture without slowing workflows
- Training staff on phishing awareness without causing alarm fatigue
- Justifying security investments to non-technical executives
“Security is not a feature — it’s a culture. And the systems manager is its chief advocate.” — CISO Magazine, 2024
Future Trends Shaping the Role of Systems Manager
The future of the systems manager role is being reshaped by automation, artificial intelligence, and evolving cybersecurity threats. Those who embrace change will lead the next generation of IT leadership.
Rise of AI and Machine Learning in System Management
AI is transforming how systems are monitored and maintained. Predictive analytics can now forecast hardware failures before they happen, reducing unplanned downtime.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Using AI to analyze log patterns and detect anomalies
- Automated incident response via AI chatbots
- Self-healing systems that reboot or reconfigure after failures
Google’s SRE (Site Reliability Engineering) model already uses machine learning to optimize system reliability at scale.
Shift Toward Cloud-Native and Hybrid Environments
More organizations are adopting hybrid models, combining on-premise infrastructure with public and private clouds. Systems managers must now master multi-cloud orchestration and cost optimization.
- Using Kubernetes to manage containerized applications across clouds
- Implementing FinOps practices to control cloud spending
- Ensuring consistent security policies across environments
The Cloud Academy reports that 89% of enterprises now use a multi-cloud strategy, increasing the complexity faced by systems managers.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
What does a systems manager do?
A systems manager oversees the planning, implementation, and maintenance of an organization’s IT infrastructure. This includes managing servers, networks, cloud platforms, and security systems to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
What skills are required to become a systems manager?
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Key skills include technical proficiency in operating systems and cloud platforms, scripting and automation, problem-solving, cybersecurity knowledge, and leadership abilities. Certifications like CompTIA Server+, Microsoft Azure, or RHCE are highly beneficial.
How is a systems manager different from a network administrator?
While a network administrator focuses on connectivity and network performance, a systems manager has a broader scope, overseeing the entire IT ecosystem — including servers, storage, applications, and security — ensuring all components work together seamlessly.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
What industries need systems managers?
Virtually every industry relies on systems managers, especially healthcare, finance, education, government, and e-commerce. Any organization with a digital infrastructure requires skilled systems management to maintain operations.
What is the future of the systems manager role?
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
The role is evolving with trends like AI-driven operations, cloud-native architectures, and Zero Trust security. Systems managers who embrace automation, continuous learning, and strategic thinking will remain indispensable in the digital age.
The role of a systems manager is more critical than ever in today’s technology-driven world. From ensuring system uptime to defending against cyber threats, they are the backbone of organizational IT. As technology evolves, so too must the systems manager — adapting to cloud, AI, and automation while maintaining the stability and security that businesses depend on. Whether you’re aspiring to become one or looking to understand their value, recognizing the depth and breadth of this role is key to appreciating modern digital operations.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Further Reading: